Glossary of Vulture Terms
We're celebrating Vulture Week because this Saturday, September 5th, marks International Vulture Awareness Day (IVAD). This commemorative day has been celebrated since at least 2009 and aims to highlight the importance of vultures and vulture conservation through education.
In today's post we're sharing some keywords that pertain to vultures. This vulture glossary also includes definitions that apply to other bird families, but are important topics to understand when learning about vultures.
Carrion
If you're going to be talking about vultures, you are inevitably going to be talking about carrion, because that is what most vultures eat. Carrion is the decaying flesh of a dead animal. Other scavengers that consume carrion besides vultures include eagles, opossums, coyotes, and some beetles.

Convergent Evolution
Vultures in the New World (the Americas) are not closely related to Old World (Europe, Asia, and Africa) vultures. Since many vultures of both types have similar features like bald heads and scavenger behavior, how can it be that they are not closely related? The answer is convergent evolution. Broadly, this refers to organisms evolving similar traits while lacking a common ancestor. Birds, flying insects, and bats are not related, but they have all evolved the capacity to fly. Similarly, vultures in both the Old and New Worlds have evolved special traits to help them specialize in feeding on carrion. With few exceptions, no matter their location, vultures fill a similar niche in the ecosystem.
Crop
The crop is an expandable part of the digestive tract of birds and some other animals. The muscular pouch, close to the throat, is used to store food before digestion. The full crop of the Lappet-faced Vulture can hold up to 3.3 lb of meat!
Gorge
Vultures are known to gorge themselves at feeding sites. They will eat until their crop is completely full, and then sit full, digesting their food. It is thought that vultures sometimes gorge themselves to the point of being unable to fly.
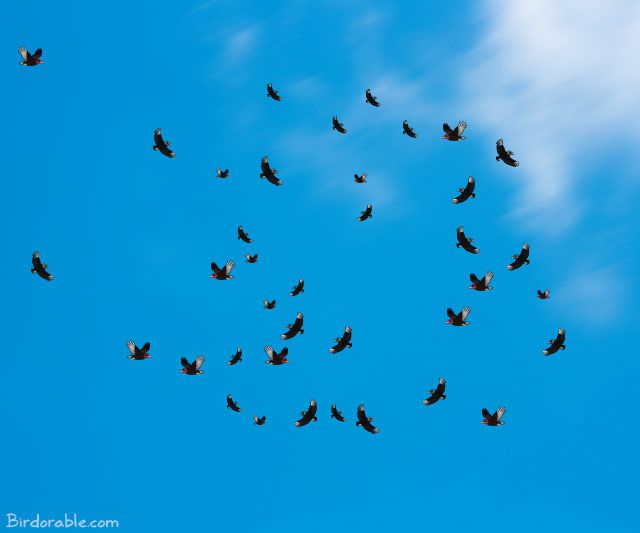

Kettle
A group of vultures in flight together, particulary soaring on thermals, is known as a kettle. Kettle may describe other birds flying in this way, including mixed flocks which may or may not have vultures.
Preening
Preening is the act of cleaning or grooming. Birds, including vultures, preen themselves to keep their feathers in top shape. Allopreening refers to social grooming between multiple individuals, often performed to strengthen social bonds. Black Vultures are known to take part in allopreening at roosting and feeding sites. Often allopreening concentrates on the head area, a spot that a bird cannot easily reach with its own beak.

Stomach Acid
Vultures have extremely corrosive stomach acid, which helps them to safely digest dead animals that may be infected with diseases and toxins. The stomach acid protects the birds from contracting and spreading disease. Gut bacteria in vultures helps them to withstand several kinds of toxins that may be found in decaying flesh.
Taxonomy
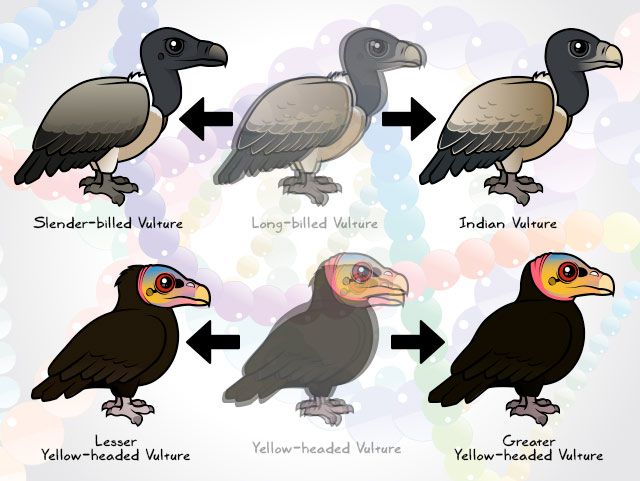
Taxonomy is a scientific system for naming and organizing living things which share certain characteristcs. The taxonomy of vultures can be confusing. New World and Old World vultures aren't closely related, despite their physical and behavioral similarities. Some scientists think that New World vultures are closely related to storks. With new advances in the study of DNA, sometimes single species are split into distinct species. The Long-billed Vulture was split into two distinct species: the Slender-billed Vulture and the Indian Vulture. The Yellow-headed Vulture was split into two species in the 1960s: the Lesser and Greater.
The big day is almost here! Tomorrow our Vulture Week will conclude on International Vulture Awareness Day!





Comments
Leave a comment
Thank you!