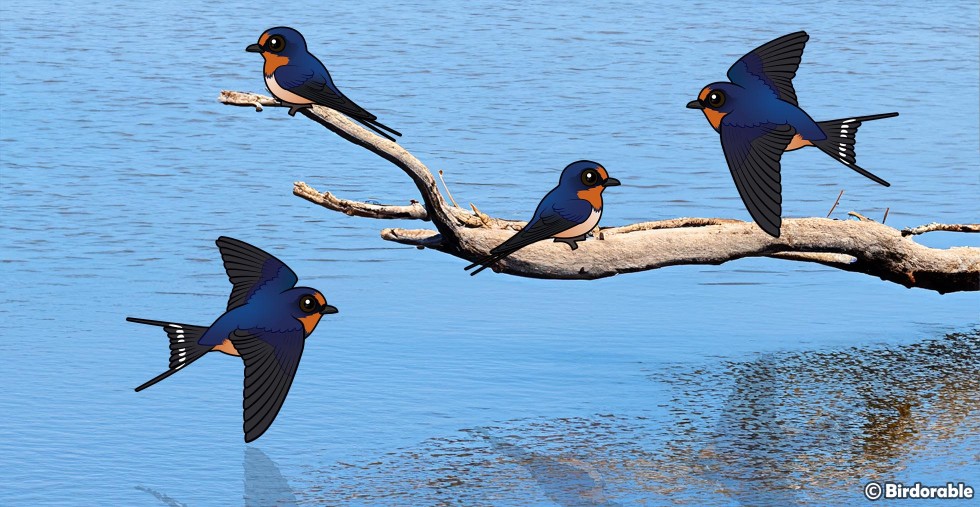
Birdwatching has become a delightful pastime for many, bringing joy and a sense of connection to nature. Among the many feathered friends we encounter, one particularly charming and widespread species stands out: the Barn Swallow. This nimble bird, known for its graceful flight and acrobatic skills in catching flying insects, is a marvel of the avian world.
The Barn Swallow's cosmopolitan presence stretches from the landscapes of Europe and the vast expanses of Asia, to the rich biodiversity of Africa and across the diverse Americas. This bird has adapted to a variety of habitats, making it a familiar sight in both rural and increasingly, urban areas. What's fascinating is how it's intertwined with human structures; it builds its cup-shaped nests predominantly in man-made structures like barns, stables, and under bridges, showcasing a remarkable coexistence with humans.
Apart from their fascinating behaviors and cultural significance, Barn Swallows are visually striking. They are characterized by their iridescent blue back, orange-red throat, and a long, deeply forked tail that makes them easily distinguishable from other birds. Watching a Barn Swallow dart and dive through the air is a mesmerizing sight, a testament to the agility and beauty inherent in the natural world.
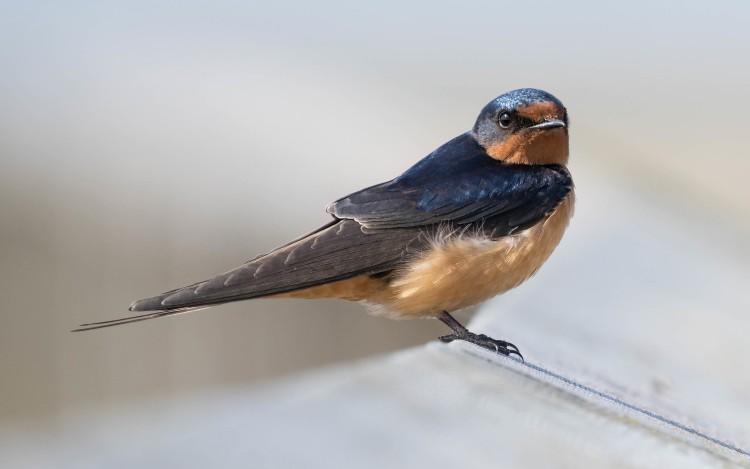

Barn Swallow by marneejill (CC BY-SA 2.0 DEED)
Their presence almost everywhere in the world speaks volumes about their adaptability and the role they play in ecosystems. As insectivores, Barn Swallows perform a crucial function by controlling insect populations, benefiting agriculture and reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Their global journey also brings them into the sphere of migration studies, with scientists tracking their movements to understand patterns that have implications for climate change research and conservation efforts.
For those who share their homes and surroundings with Barn Swallows, there's an opportunity to observe these birds up close. Their nesting behavior, especially in accessible structures, offers a unique insight into their world. Observing how they meticulously build their nests, care for their young, and interact with their environment provides invaluable lessons in resilience, community, and the interdependence of species.
Whether you're a seasoned birdwatcher, a casual observer, or someone fascinated by the seamless integration of wildlife into our daily lives, the Barn Swallow offers endless opportunities for discovery and delight. The next time you see a swift, graceful bird darting through the sky or skimming the surface of a water body, take a moment to appreciate the remarkable Barn Swallow.
The title of this article is actually a quote from a movie in which James Stewart goes out birdwatching and every time he asks his companion "What kind of bird is that?", the answer is always "Barn Swallow!". Do you know what movie I'm talking about?
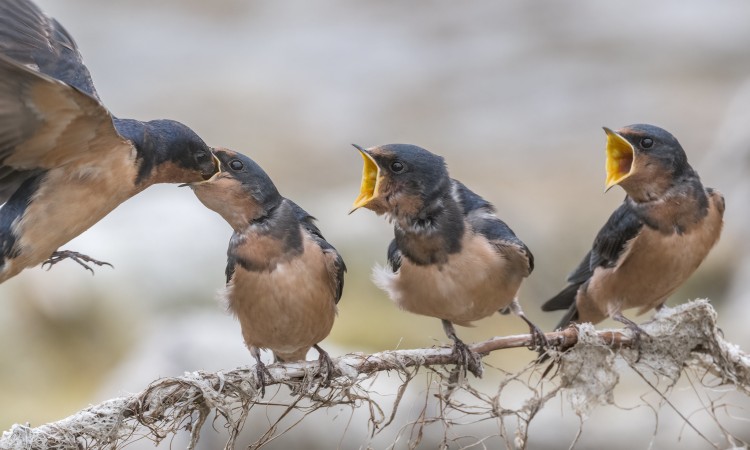

Barn Swallows being feed by Becky Matsubara (CC BY 2.0 DEED)