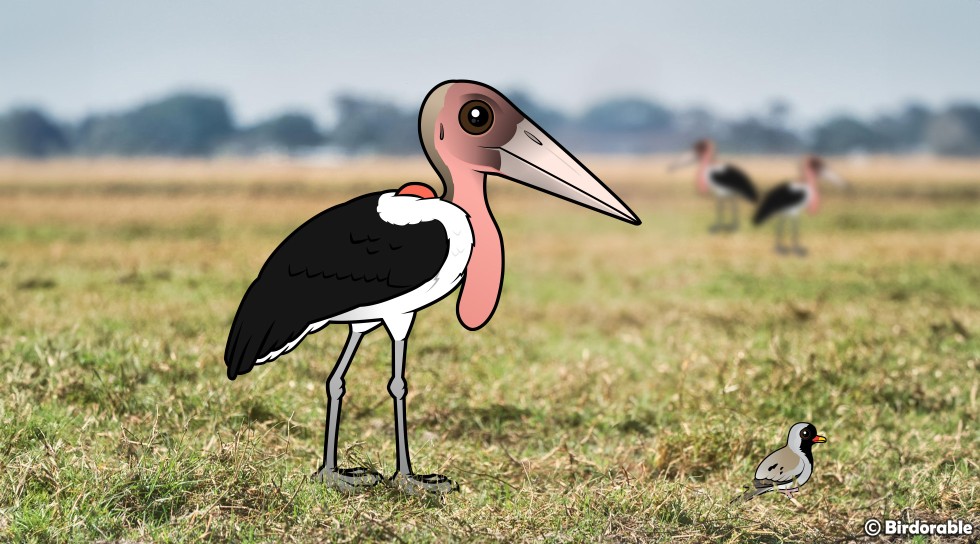
The Marabou Stork is one of those birds that might not win any beauty contests but is absolutely fascinating in terms of behavior, adaptation, and sheer size. With the largest wingspan tied with the Andean Condor, reaching an impressive 10.5 feet, it's a sight that can leave anyone in awe. These birds, found throughout tropical Africa south of the Sahara Desert, have an intriguing presence that's hard to ignore.
What makes the Marabou Stork stand out, aside from its massive wingspan, is its peculiar appearance. They have a mostly bald head, which can be an unusual sight compared to the more feathery heads of other birds. Additionally, they sport two inflatable air sacs around their neck, which adds to their unique look. This appearance is perfectly suited to their lifestyle and habitat.
The Marabou Stork is a master of adaptation. They thrive in close proximity to humans, a trait not common among many species. This adaptability has led to an increase in their population in some areas, as they make the most out of the opportunities provided by human activities. Their diet further shows their adaptability. Needing to consume more than 1.6 pounds (0.725 kilograms) of food daily, they are not picky eaters. These birds are scavengers, eating anything they can find or catch, including the animals fleeing from grass fires. This opportunistic feeding strategy might seem a bit unscrupulous, but it's a brilliant display of adaptability and survival.
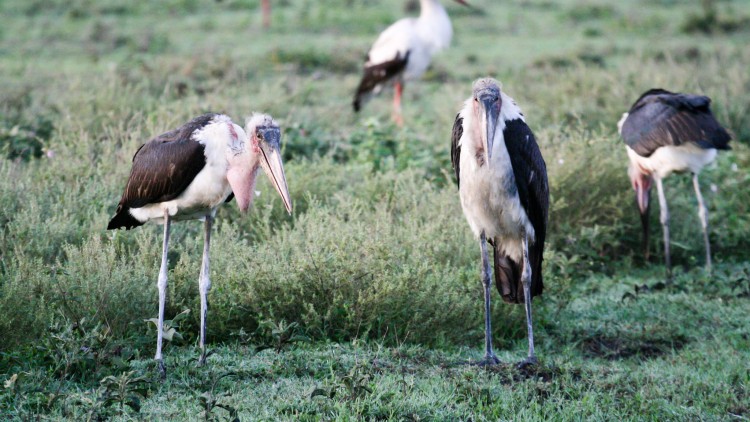

Marabou Storks near Ndutu Lodge, Serengeti, by Christoph Strässler (CC BY-SA 2.0 DEED)
Witnessing a Marabou Stork in flight is an unforgettable experience. On a personal note, seeing one soar overhead during our trip to The Gambia was a magnificent moment. Despite their less-than-cuddly appearance, the grace with which they navigate the air is truly a spectacle. Their enormous wingspan allows them to glide effortlessly, a remarkable sight against the backdrop of Africa's skies.
Their relationship with humans is notably ambivalent. On one hand, their ability to adapt to human environments means they can thrive in areas where other species might struggle. On the other hand, this closeness brings them into conflict with people, especially in urban areas where they are often considered pests due to their scavenging nature.
Conservation-wise, the Marabou Stork is doing relatively well compared to other bird species. Their adaptability and broad diet mean they are less susceptible to the threats of habitat loss and climate change that menace many other birds. However, this does not mean they are without challenges. Pollution, particularly plastic waste, poses a significant threat to these birds, as it does to all wildlife that relies on scavenging. The Marabou Stork is a bird that embodies the concept of survival against the odds. Its ability to adapt to various environments, coupled with its unique appearance and behaviors, makes it a fascinating subject of study and observation.
Watch this fascinating video of Marabou Storks toying with a fish, only for an African Fish Eagle to suddenly swoop in and snatch it away. A reminder not to play with your food: