We're celebrating Vulture Week because this Saturday, September 5th, marks International Vulture Awareness Day (IVAD). This commemorative day has been celebrated since at least 2009 and aims to highlight the importance of vultures and vulture conservation through education.
Vulture week rolls on with some cool vulture facts. These extreme facts show how diverse this amazing family of birds can be.
Largest Vulture
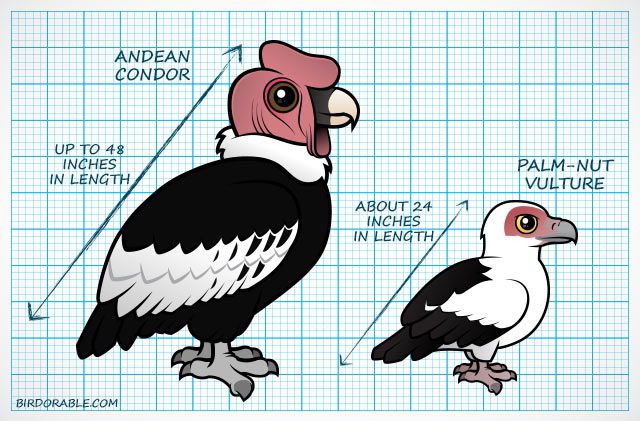
Among New World vultures, the Andean Condor and California Condor can both reach up to 48 inches in length, and weigh 26 pounds or more. In the Old World, the Cinereous Vulture reaches up to 47 inches in length. Female Cinereous Vultures may weigh up to 31 pounds!
Smallest Vulture
In the Old World, the Palm-nut Vulture has this record. They only grow to be about 24 inches long and weigh just around 3.5 pounds. The Lesser Yellow-headed Vulture is the smallest in the New World, reaching between 22 and 24 inches in length.
Vulture Longevity Records
The longest lived Eurasian Griffon reached over 41 years of age in captivity. A captive-raised Lammergeier lived to be over 45 years old. The Andean Condor is believed to be capable of living 50 years or more in the wild. A captive Andean Condor that lived at a zoo in Connecticut lived 79 years! The longevity record for a wild Turkey Vulture is over 17 years, while a wild Black Vulture reached over 25 years of age.
Most Abundant Vulture
The Turkey Vulture is the most abundant species of vulture in the world, with a population that probably numbers into the millions of individuals.

Fastest Decline
Many vulture species in Africa and on the Indian subcontinent are in peril. The population decline of the White-rumped Vulture is an unfortunate example of this. In the mid 1980s, the White-rumped Vulture was considered to be the most abundant large bird of prey in the world. Since that time, the species has declined rapidly, losing up to 99.9% of its total population in just 20 years.
Longest Migration
Most vulture species are sedentary, year-round residents throughout their range. In the New World, the Turkey Vulture is the only vulture spcies that has regular seasonal migration. Birds that breed in southern Canada probably travel at least 1,000 miles to reach their wintering grounds to the south, traveling around 100 miles per day of migration. In the Old World, Egyptian Vultures may travel up to 5,500 miles when they migrate from their breeding grounds to their wintering grounds at the southern end of the Sahara Desert.
Ancient Birds
Relatives of vultures have existed for millions of years. Early ancestors of Old World vultures, in the now extinct Diatropornis family, existed in the Eocene epoch about 56 to 38 million years ago.
Highest Flyer
The Rueppell's Vulture of Africa is thought to be the world's highest flying bird. It has been recorded flying at an altitude of 11,300 meters or 37,000 feet above sea level!
Can't get enough of these amazing and important birds? Be sure to check out our great collection of cute and original vulture apparel and gifts.